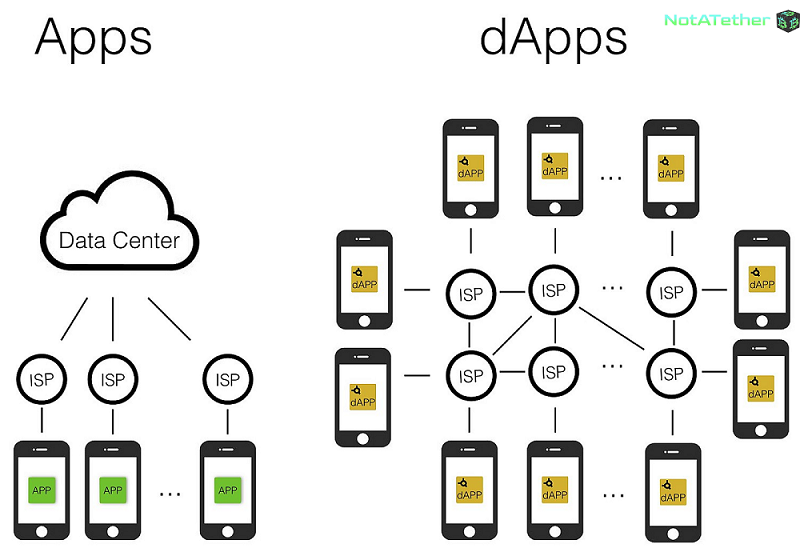
What is Decentralized Applications (DApps)?
Decentralized applications (DApps) are programs that run on a blockchain or P2P network of computers. They are unlike centralized applications running on a computer.
These programs have existed since the advent of P2P networks and they are outside the purview and control of any organization or a single person. A standard web app, for example, runs on a computer system that belongs to a specific organization and person, and these people have complete control over the program and its operation. So the backend is controlled by a single organization.
DApp Frontend
For dApps, the frontend code runs on the user side and represents what you see. They look like mobile apps that have a digital wallet with the following information:
- Contains a file containing the user’s private and public keys, which are used to authenticate the user.
- Cryptographic keys and the blockchain addresses interact with the blockchain network.
- Enables the backend (smart contracts) to execute.
DApp Backend
The backend code (smart contract) runs on the server-side of the application and represents the entire business logic. The backend code is stored and parsed on the blockchain and is open source, it also performs a similar function regardless of the execution environment.
DApps in Various Industries
Decentralized applications can be used in various industries such as decentralized exchanges, gaming, advertising networks, etc. It takes control out of the management or ownership of a third party.
DApps in The Field of Digital Currencies
In the world of digital currencies, dApps run in a blockchain network and in a public, decentralized, open-source environment. Running these dApps in a decentralized manner protects them from any third-party reference.
Do Decentralized Applications Need Blockchain?
Decentralized applications can also run on a P2P network and no longer require a blockchain. Also, active users in this network can consume content, feeding or seeding content, or both at the same time. Examples of these programs include the following:
- Tor Browser
- Popcorn Time
- BitMessage
- BitTorrent
Advantages of decentralized applications
User Privacy
User information is stored in a shared database that is not controlled by any authority or organization, and this information is only decrypted by the user.
Costs
The cost of centralized applications is much higher. Decentered applications can be more financially efficient because they operate without intermediaries to make a profit from transactions.
Data Security
In a centralized system, if the server is hacked, all user information, including addresses, files and videos, and photos and messages, many of their important information may be stolen. But in decentralized applications that are decentralized, this does not happen.
Point Of Failure
In centralized applications, if the server crashes, the application network goes offline, and users can only access the application after fixing the error. But this is not the case in decentralized applications, and users’ machines do not depend on a central server to perform processes.
Content Guidelines
Centralized applications are limited by certain rules. For example, some videos are banned from YouTube or some countries do not have access to YouTube. But in a decentralized applications program there is no such thing and no reference can be censored and only users are responsible for its consequences.
Challenges Of Decentralized Applications
- Difficult to maintain: When code is deployed on a blockchain, it is not possible to delete or edit it. Therefore, there will be problems for developers to update or troubleshoot DApp.
- Network congestion: Current networks process 10-15 transactions per second. So if a DApp uses too many computational resources, the whole network becomes congested.
DApps examples
- BitTorrent
- Augur
- Golem
- Melonport
- OMG Network